

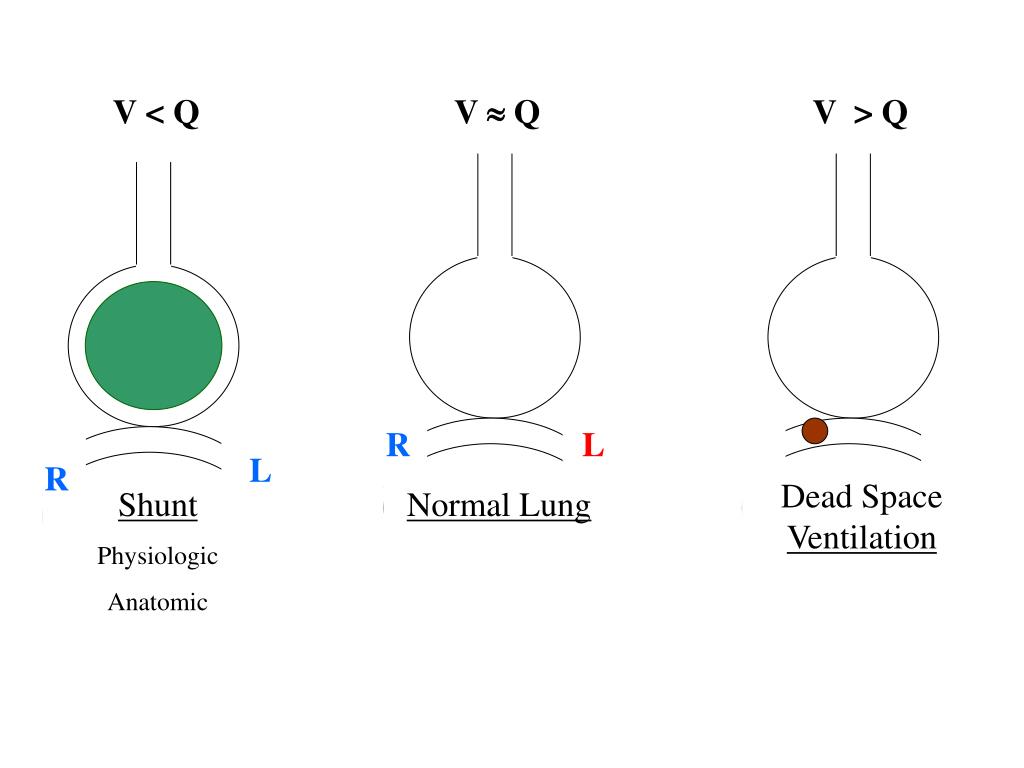
How does intrapulmonary shunt improve oxygenation? Bubbles are not normally observed in the absence of vascular dilatation because lung capillaries act as filters. Intrapulmonary shunting is most commonly demonstrated by contrast TTE when bubbles from agitated saline are visualized in the left atrium within 36 beats after being noted in the right side of the heart. How is an intrapulmonary shunt diagnosed? Because pulmonary embolism (PE) alters perfusion rather than ventilation, it does not create an intrapulmonary shunt. Intrapulmonary shunting occurs when perfusion is maintained to nonventilated alveoli. A right-to-left shunt allows deoxygenated systemic venous blood to bypass the lungs and return to the body.
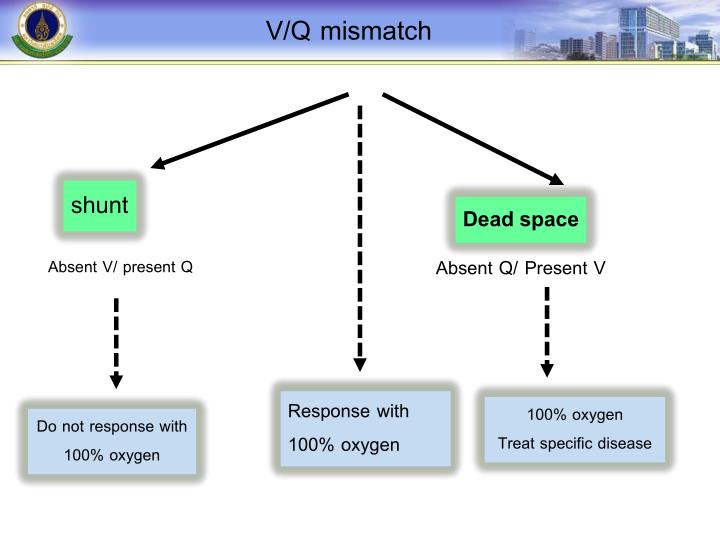
What does right to left intrapulmonary shunting mean?Ī shunt is an abnormal communication between the right and left sides of the heart or between the systemic and pulmonary vessels, allowing blood to flow directly from one circulatory system to the other. The deoxygenated blood (mixed venous blood) bypasses the ventilated alveoli and mixes with oxygenated blood that has flowed through the ventilated alveoli, consequently leading to a reduction in arterial blood content. Shunt is defined as the persistence of hypoxemia despite 100% oxygen inhalation. Causes of shunt include pneumonia, pulmonary edema, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), alveolar collapse, and pulmonary arteriovenous communication.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
